Components
Modals
Modal Dialogs
In general, creating or editing objects can happen in one of two ways.
- Lead the user to the new or existing record.
- Within a modal window.
Modal Rules
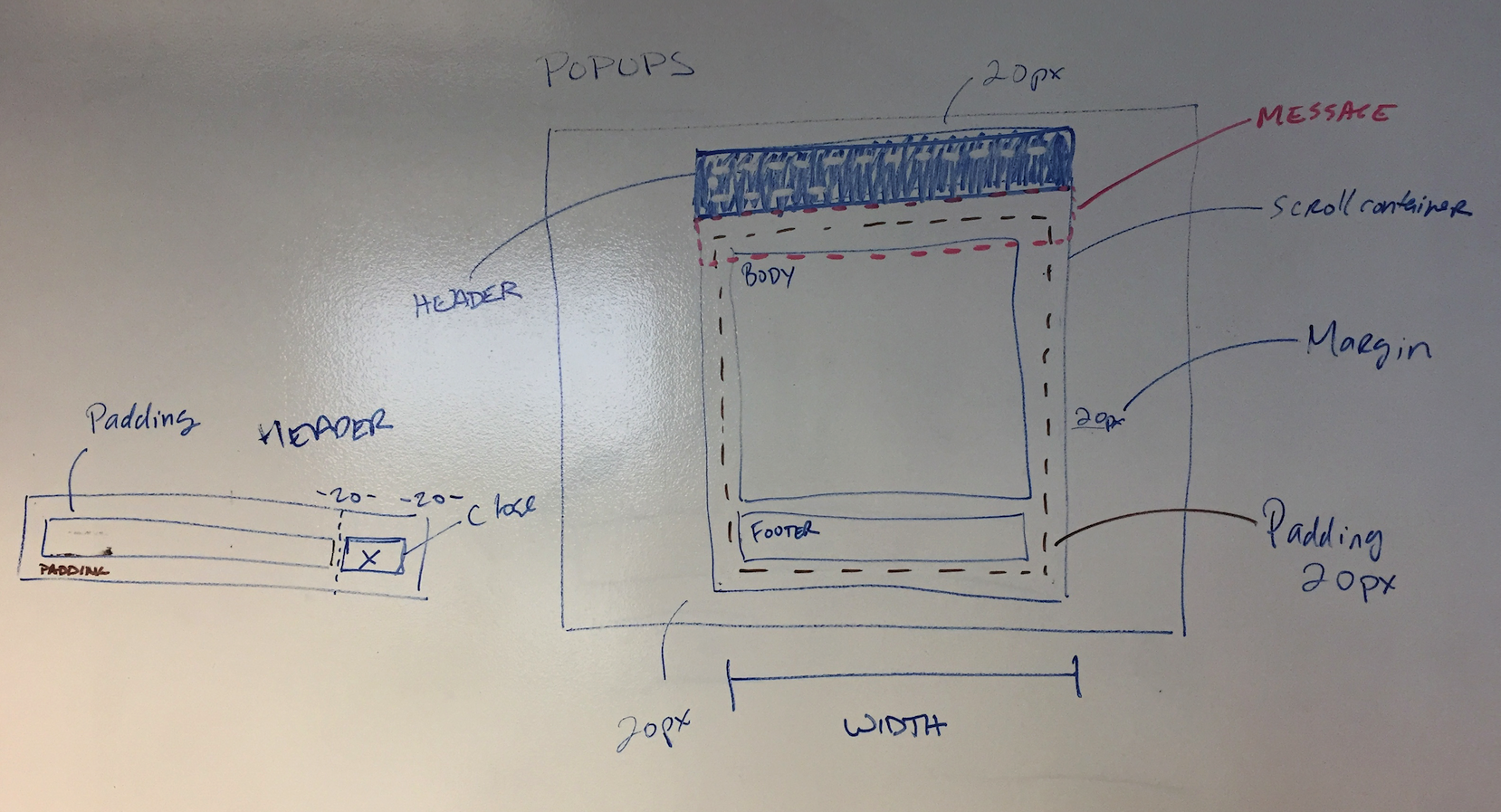
- Use the browser to scroll to see the full content of the modal.
- As a rule, do not add scrollbars inside the modal content area.
- On small screens, the modal should take up 100% width and height of the device.
- Always include a "close" button in the header.
- Allow cancelling by clicking outside of the modal. Unless there is a specific business reason not to.
You may consider using a modal window when you need to:
- Update or add an object when you do not want to lose the user’s current context, or want to add multiple objects sequentially. Example: Add investigator
- Create or edit a record with a simple form. Example: Add new note
- Step through a simple wizard. Example: Import a bundle
- Once complete, you change context of the level above. Example: Add new application.
- Generally, any “create” action that has a “not-too-complex” form should be done in a modal.
- If an action will destroy any work (I.E. deleting an object) using an intrusive modal is good practice.
- Do not use modals to show error or success messages. Use same-page “messages” instead.
After actions have been taken
When presenting a modal to create a new sibling or child object, on create, there are a few next-step options.
- Create the object and stay in present state, updating the current view with the new record and/or introducing a toast to indicate successful action.
- If the created object spawns additional options for editing, direct the user out of the current page and lead the user to the newly-created object. This can be done in a new tab or on the same tab, depending on if a context switch confuses the user.
- If the created object is initiated by an “add” action in a windowed tab, add the object and then focus on the newly-created tab.
Note: Object add forms not in a modal: When the form/process for adding a new object goes to a separate page (replacing the list view), on create, the user is returned to the list with the new object added.
Anatomy of a Modal
- Header
- Sub-title (little title context of what generated the modal)
- Title (big title describes the action)
- Close Button
- Message
- Content Container
- Content
- Footer
- Primary and Secondary Action Bars
Modal Pieces